Conveyor belts are the backbone of several industries around the world. They help transport goods from one place to another efficiently. But what ensures their smooth operation? The answer lies in the conveyor belt components, each with a specific role and function. Even with a single missing or faulty part, the conveyor belt will be unable to function.
Every part works together to ensure flawless performance and prevent wear. Understanding the function and workings of each component is key. It helps you maintain the system and resolve minor issues. So, what are these essential components, and how do they work? This guide will give you all the insights you need. So, let’s get started!
Key Components of Conveyor Belts
As I said above, there is a network of components behind every efficient conveyor belt. All those parts are carefully designed to run the conveyor belt smoothly. So, let’s look at those key components and their working.
1- Conveyor Belt (Belt)

The belt is a significant component of conveyor belts. It is a continuous loop stretched around two pulleys and moves continuously. The belt is responsible for moving goods from one place to another. It can be made with different materials depending on the needs of industries. For example, some belts are made of rubber and are used in mining industries for flexibility.
Other materials used for belts include PVC, metal, and fabrics such as nylon and cotton. Moreover, conveyor belts come in different types depending on their structure. For instance, flat belts have smooth and straight surfaces. Other belt types include modular, inclined, cleated, and curved belts, each with a unique appearance.
2- Pulleys

Pulleys are wheel-like structures that rotate and provide force to the belt, helping it move. The conveyor system has a set of pulleys, each performing a specific function. Let me explain them in simple words. The first pulley is known as a driver or head pulley. It is attached to the motor and transfers the power to the belt. This pulley is at the end of the belt, from where goods exit.
The second pulley, called an idler pulley, is on the opposite side of the driver pulley and does not provide power but just supports the belt. Another pulley is a snub pulley, which is located near the driver pulley and prevents the belt from slipping. The fourth one is a bent pulley that helps the belt change direction. The last one is the take-up pulley, which helps adjust the tension.
3- Drive Motor
The driver motor is the heart of the conveyor belts. Without this motor, the conveyor belt would be unable to move, as it powers the whole system. It receives the power from an external source such as a battery or power supply. The motor converts this electrical energy into mechanical energy by rotating a shaft.
This mechanical energy is transferred to the driver pulley, which moves the belts. Different types of conveyor belts use different motors. For example, AC motors use alternating currents and provide steady and continuous movement. DC motors use direct current and provide variable speed and control. Lastly, some industries use pre-programmable server motors.
4- Belt Tensioners
Tension is a crucial factor for the smooth movement of conveyor belts. Without proper tension, the belt will be loose, slip, and cause conveyor belt damage. That’s where the belt tensioners come into the scene. This component keeps the belt tight enough to prevent slipping or losing. However, it also ensures that the belt is not too tight to move.
As you know, belts become loose over time due to loads. So, tensioners adjust and maintain the tension. They come in various types, such as manual tensioners, which you can adjust by hand. Other types include automatic ones, which use a spring or hydraulic system to adjust the tension automatically. However, gravity tensioners use weight to maintain belt tension.
5- Rollers (Idler Rollers)
One of the most important components of conveyor belts is rollers. They are cylindrical rods that support the belts and are present at regular intervals along the conveyor frame. Unlike pulleys, rollers do not move the belt but reduce friction and help ensure smooth movement. A motor does not power them, but they rotate freely and distribute loads evenly over the belt.
A conveyor system always has a set of rollers, each performing a unique task. For example, carrying rollers are on the top of the belt and support the carrying section. Return rollers are located at the bottom and hold the returning section after unloading. Impact rollers contain rubber rings and absorb shocks during loading.
6- Conveyor Frame
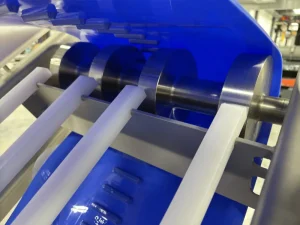
The conveyor frame is like a skeleton that supports all other components. It provides a base for different parts to work and helps ensure the proper functionality of a conveyor belt. For example, it supports the pulleys’ rotation and helps move the belts. Moreover, the frame also prevents unwanted vibration during loading and unloading.
Conveyor frames come in various types depending on their material. For example, steel frames are more durable and strong and can handle heavy loads. Aluminum frames are lightweight and are used in portable conveyor belts. Further, stainless steel frames are specially designed for food industry conveyor belts. Lastly, rubber frames are non-rusting and are used in smaller conveyor belts.
7- Conveyor Belt Cover
As you know, belts remain in continuous movement and transport different objects. So, they are more likely to rust and damage over time. Here, the conveyor belt covers act as a protective shield and increase the belts’ lifespan. For example, they protect the belt from stains, moisture, and environmental factors. They also help the belt maintain its structural integrity by protecting it from abrasion.
Conveyor belt covers come in several materials depending on their usability. Rubber covers are flexible and protect the belt’s surface from abrasion by rough materials. PVC covers are affordable and ideal for belts that often handle chemicals. Polyurethane belt covers protect the belt from heat and are best for outdoor conveyor belts.
8- Conveyor Belt Cleaner (Scraper)
Scarpers are one of the essential components in maintaining the lifespan of conveyor belts. As you know, belts handle various types of material every day. So, different debris and dust particles stick to the surface of the belt. As a result, they hinder smooth movement and cause damage. For this purpose, different scarpers are installed to clean the conveyor belts.
The list of some common scarpers includes:
- Primary Belt Cleaners: They are present on the head of the driver pulley. These cleaners remove large debris that sticks to the upper surface of the belt.
- Secondary Belt Cleaners: They come just after the primary cleaner and are present on the return side of the belt. They remove the leftover debris and provide fine cleaning.
- Tertiary Belt Cleaners: This is an extra cleaner in a food industry conveyor belt. They clean the dust particles to add cleanliness to food items.
- Rotary Belt Cleaners: These cleaners have sharp blades that rotate continuously. It moves against the belt surface and removes the sticky debris.
9- Sensors and Controls
Sensors and controls are essential components in modern conveyor belts. This system ensures that each part works efficiently. In case of any misalignment or issue, it detects the problem and lets the operator make adjustments. For example, proximity sensors ensure the correct amount of goods is loaded onto the belt.
However, photoelectric sensors use a beam of light to detect the object. In case of any issue, they send signals to the control system to take action. These sensors mainly control the direction of the goods. Moreover, speed sensors detect the accurate speed of the conveyor belt. Lastly, weight sensors measure the weight the belt carries and detect overload.
10- Hopper or Chute
The hopper or chute is a vital part of conveyor belts for loading and unloading materials. It is a funnel-like structure located at the top of the belts. A hopper has two openings: a broad opening and a narrow(chute) opening. Materials such as powders and grains are poured from the wide opening.
These materials discharge from the chute and are sent to storage areas. Hoppers help maintain the flow of fine materials and prevent them from spreading. They come in several types, such as vibratory hoppers, with vibrating mechanisms to ensure smooth flow. Other types include gravity, straight, and curved hoppers.
11- Side Guards
As the name suggests, side guards are protective barriers along the edges of conveyor belts. These barriers prevent material from dropping and ensure safe transfer. Almost all types of conveyor belts have these guards, but they vary in materials. For example, metal guards are mainly made of aluminum and steel. They are durable and used in heavy-duty conveyors.
However, rubber and plastic guards are lightweight and suitable for light-duty operations. If we discuss their types, side guards come in three types. The first one is fixed guards that are permanently attached to the conveyor belts. The second type is adjustable, which allows you to adjust its width and height. The last one is flexible guards that allow slight movement.
12- V Guides
V guides are small raised strips at the bottom of conveyor belts. These guides are like train tracks that keep the belt in place. They prevent the belt from slipping from the roller and keep it moving in one direction. Without V guides, the belt might shift to one side, which can cause misalignment and damage.
There are three types of V guides. The first is a molded V guide installed during the conveyor belt’s manufacturing. The other type is customizable welded V guides, which can be installed later. The last one is inserted V guides that are present into pre-cut grooves of conveyor belts. This type of V guide is removable and can be replaced easily.
How do All Components Work Together to Move Materials?
I hope you understand each component and how they work. Right? Now, let’s discuss how all these components work together to transfer the goods.
When the motor turns on, it powers the driver’s pulley. This pulley pulls the belt, which moves on the rollers. Carrying rollers support the top part of the belt, while return rollers support the bottom part. The belt starts moving at a constant speed. However, if it is loose, tensioners adjust the tightness and prevent it from slipping.
At the same time, V guides keep the belt on the track, and side guards support the material. They prevent the material from slipping on any side and ensure smooth movement. Sensors monitor the whole conveyor system. If they find any misalignment or change in speed, the system automatically stops. Lastly, a belt cleaner removes the debris after unloading the goods.
Conclusion
Conveyor belts are a convenient way of transferring different goods from one place to another. They operate with a proper working system containing other components. In this article, I have discussed the details of each element. For example, belts are flat surfaces that carry the goods. With the help of pulleys, these belts move continuously.
A motor drives the whole system and is known as the heat of conveyor belts. Moreover, a series of rollers ensures the smooth movement of the belt. Along with the roller, V guides direct the belt onto one track. Lastly, side guards prevent the object from falling. All these components work together and transport material across various operations.
